Create Class Diagram using Open API
![]() Class Diagram from Unified Modeling Language is a typical diagram used to model the structure of a system. Class Diagram is one of the major diagram in object oriented modeling. The classes being modeled in class diagram can become the main objects in your system, describing the interactions of the application as well as the classes needed to be implement. Instead of creating class diagram manually, you can also create it programmatically using Open API. In this article we will show you how to create class diagram with Visual Paradigm’s Open API.
Class Diagram from Unified Modeling Language is a typical diagram used to model the structure of a system. Class Diagram is one of the major diagram in object oriented modeling. The classes being modeled in class diagram can become the main objects in your system, describing the interactions of the application as well as the classes needed to be implement. Instead of creating class diagram manually, you can also create it programmatically using Open API. In this article we will show you how to create class diagram with Visual Paradigm’s Open API.
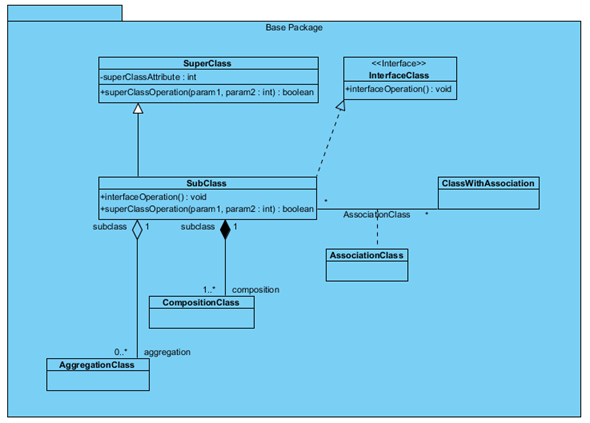
This is the class diagram which we are going to create. The diagram consists of a package, several classes where some with attributes and operations, and also the popular relationships on class model, association, generalization, realization as well as association class. Let’s start with create a blank class diagram.
Create Blank Class Diagram
We can use the DiagramManager.createDiagram operation to create a blank new diagram.
DiagramManager diagramManager = ApplicationManager.instance().getDiagramManager(); IClassDiagramUIModel diagram = (IClassDiagramUIModel) diagramManager.createDiagram(DiagramManager.DIAGRAM_TYPE_CLASS_DIAGRAM);
Creating Diagram and Model Elements
Once the diagram is created, we can then move on to create the diagram elements and model elements. Our diagram include a package, 7 classes where one is an Interface, attributes and operations, generalization, realization, association, aggregation, composition as well as association class.. Creating model elements involve the 4 major steps:
- Creating object instance of the model element
- Specify the properties of the model element, i.e. name, description, etc…
- Create shape instance of the model element
- Specify the properties of the shape, i.e. location, color, etc…
We first create the package. To create package:
// create base package model
IPackage basePackage = IModelElementFactory.instance().createPackage();
basePackage.setName("Base Package");
// create base package shape
IPackageUIModel basePackageShape = (IPackageUIModel) diagramManager.createDiagramElement(diagram, basePackage);
basePackageShape.setBounds(94, 79, 717, 516);
// set to automatic calculate the initial caption position
basePackageShape.setRequestResetCaption(true);
Now the package is created, and we can move on to create classes. We first create the superclass as well as its attributes and operations.
// create superclass model
IClass superClass = IModelElementFactory.instance().createClass();
superClass.setName("SuperClass");
basePackage.addChild(superClass); // add superClass as child of the package
After create class model, we can then create attribute for the superclass.
// create attribute for superclass model
IAttribute attribute = IModelElementFactory.instance().createAttribute();
attribute.setName("superClassAttribute");
attribute.setType(typeInt);
attribute.setVisibility(IAttribute.VISIBILITY_PRIVATE); // specify it is a private attribute
superClass.addAttribute(attribute); // add attribute to class
Next we create the operation and parameters.
// create operation for superclass model
IOperation superclassOperation = IModelElementFactory.instance().createOperation();
superclassOperation.setName("superClassOperation");
superclassOperation.setVisibility(IOperation.VISIBILITY_PUBLIC); // specify it is a public operation
superclassOperation.setReturnType(typeBoolean); // specify the return type of the operation
// define parameters for operation
IParameter parameter1 = IModelElementFactory.instance().createParameter();
parameter1.setName("param1");
parameter1.setType(typeString);
superclassOperation.addParameter(parameter1); // add parameter to operation
IParameter parameter2 = IModelElementFactory.instance().createParameter();
parameter2.setName("param2");
parameter2.setType(typeInt);
superclassOperation.addParameter(parameter2);
superClass.addOperation(superclassOperation); // add operation to class
When class model is ready we can then create class shape for it.
// create superclass shape IClassUIModel superClassShape = (IClassUIModel) diagramManager.createDiagramElement(diagram, superClass); superClassShape.setBounds(208, 144, 274, 57); basePackageShape.addChild(superClassShape); superClassShape.setRequestResetCaption(true);
The first superclass is created, next we go to create the interface class and operation.
// create interface class model
IClass interfaceClass = IModelElementFactory.instance().createClass();
interfaceClass.setName("InterfaceClass");
basePackage.addChild(interfaceClass);
// specify the stereotype as "Interface"
interfaceClass.addStereotype("Interface");
// create operation for interface class
IOperation interfaceOperation = IModelElementFactory.instance().createOperation();
interfaceOperation.setName("interfaceOperation");
interfaceOperation.setVisibility(IOperation.VISIBILITY_PUBLIC);
interfaceOperation.setReturnType(typeVoid);
interfaceClass.addOperation(interfaceOperation);
// create interface class shape
IClassUIModel interfaceClassShape = (IClassUIModel) diagramManager.createDiagramElement(diagram, interfaceClass);
interfaceClassShape.setBounds(514, 144, 141, 53);
basePackageShape.addChild(interfaceClassShape);
interfaceClassShape.setRequestResetCaption(true);
After that we create the rest of the classes.
// create subclass model
IClass subClass = IModelElementFactory.instance().createClass();
subClass.setName("SubClass");
basePackage.addChild(subClass);
IClassUIModel subClassShape = (IClassUIModel) diagramManager.createDiagramElement(diagram, subClass);
subClassShape.setBounds(208, 294, 272, 53);
// set subclass to show inherited operations
subClassShape.setShowDerivedOperations(true);
basePackageShape.addChild(subClassShape);
subClassShape.setRequestResetCaption(true);
// create a normal class which will have normal association to subclass
IClass classWithAssociation = IModelElementFactory.instance().createClass();
classWithAssociation.setName("ClassWithAssociation");
basePackage.addChild(classWithAssociation);
IClassUIModel classWithAssociationShape = (IClassUIModel) diagramManager.createDiagramElement(diagram, classWithAssociation);
classWithAssociationShape.setBounds(632, 294, 126, 40);
basePackageShape.addChild(classWithAssociationShape);
classWithAssociationShape.setRequestResetCaption(true);
// create a normal class which will have aggregation association to subclass
IClass aggregrationClass = IModelElementFactory.instance().createClass();
aggregrationClass.setName("AggregationClass");
basePackage.addChild(aggregrationClass);
IClassUIModel aggregrationClassShape = (IClassUIModel) diagramManager.createDiagramElement(diagram, aggregrationClass);
aggregrationClassShape.setBounds(143, 521, 128, 40);
basePackageShape.addChild(aggregrationClassShape);
aggregrationClassShape.setRequestResetCaption(true);
// create a normal class which will have composition association to subclass
IClass compositionClass = IModelElementFactory.instance().createClass();
compositionClass.setName("CompositionClass");
basePackage.addChild(compositionClass);
IClassUIModel compositionClassShape = (IClassUIModel) diagramManager.createDiagramElement(diagram, compositionClass);
compositionClassShape.setBounds(271, 443, 131, 40);
basePackageShape.addChild(compositionClassShape);
compositionClassShape.setRequestResetCaption(true);
// create an association class
IClass associationClass = IModelElementFactory.instance().createClass();
associationClass.setName("AssociationClass");
basePackage.addChild(associationClass);
IClassUIModel associationClassShape = (IClassUIModel) diagramManager.createDiagramElement(diagram, associationClass);
associationClassShape.setBounds(492, 384, 102, 40);
basePackageShape.addChild(associationClassShape);
associationClassShape.setRequestResetCaption(true);
Creating Relationships
In our example we have 6 relationships, including generalization, realization, normal association, aggregation, composition as well as an association class. Let’s walk through it one by one. Creating relationships basically have the following steps:
- Create relationship model
- Specify the properties of the relationship model, i.e. name, description, etc…
- Specify the model element of From end and To end
- Specify the properties for association end, such as multiplicity, aggregation kind, etc…(For associations, composition and aggregation only)
- Create relationship connector (view)
- Specify the properties of the connector, i.e. caption position, color, etc…
Let’s start from the generalization between SuperClass and SubClass. To create the generalization:
// create generalization relationship from superclass to subclass IGeneralization generalizationModel = IModelElementFactory.instance().createGeneralization(); generalizationModel.setFrom(superClass); generalizationModel.setTo(subClass); // create generalization connector on diagram IGeneralizationUIModel generalizationConnector = (IGeneralizationUIModel) diagramManager.createConnector(diagram, generalizationModel, superClassShape, subClassShape, null);
Next we move on to create realization between interface and subclass. The steps for create realization is pretty similar with generalization.
// create realization relationship from interface class to subclass IRealization realizationModel = IModelElementFactory.instance().createRealization(); realizationModel.setFrom(interfaceClass); realizationModel.setTo(subClass); // create realization connector on diagram IRealizationUIModel realizationConnector = (IRealizationUIModel) diagramManager.createConnector(diagram, realizationModel, interfaceClassShape, subClassShape, null);
Now we move to create the simple association between SubClass and ClassWithAssociation.
// create normal association between subclass to "ClassWithAssociation"
IAssociation associationModel = IModelElementFactory.instance().createAssociation();
associationModel.setName("AssociationClass");
associationModel.setFrom(subClass);
associationModel.setTo(classWithAssociation);
// specify multiplicity for from & to end
IAssociationEnd associationFromEnd = (IAssociationEnd) associationModel.getFromEnd();
associationFromEnd.setMultiplicity("*");
IAssociationEnd associationToEnd = (IAssociationEnd) associationModel.getToEnd();
associationToEnd.setMultiplicity("*");
// create association connector on diagram
IAssociationUIModel associationConnector = (IAssociationUIModel) diagramManager.createConnector(diagram, associationModel, subClassShape, classWithAssociationShape, null);
// set to automatic calculate the initial caption position
associationConnector.setRequestResetCaption(true);
The steps for create aggregation and composition are similar to the normal association. The only different is to specify the aggregation kind on the association end.
// create aggregation association between subclass and AggregationClass IAssociation aggregationModel = IModelElementFactory.instance().createAssociation(); ... IAssociationEnd aggregationFromEnd = (IAssociationEnd) aggregationModel.getFromEnd(); // specify from end as aggregation as well as the multiplicity aggregationFromEnd.setAggregationKind(IAssociationEnd.AGGREGATION_KIND_AGGREGATION); ... // create composition association between subclass and CompositionClass IAssociation compositionModel = IModelElementFactory.instance().createAssociation(); ... IAssociationEnd compositionFromEnd = (IAssociationEnd) compositionModel.getFromEnd(); // specify from end as composition as well as the multiplicity compositionFromEnd.setAggregationKind(IAssociationEnd.AGGREGATION_KIND_COMPOSITED);
Finally we create the relationship with association class.
// create association class relationship IAssociationClass associationClassModel = IModelElementFactory.instance().createAssociationClass(); associationClassModel.setFrom(associationModel); associationClassModel.setTo(associationClass); // create association connector on diagram IAssociationClassUIModel associationClassConnector = (IAssociationClassUIModel) diagramManager.createConnector(diagram, associationClassModel, associationConnector, associationClassShape, null);
When everything is ready, we show up the diagram.
diagramManager.openDiagram(diagram);
Sample Plugin
The sample plugin attached in this article demonstrate how to create class diagram using Open API. After you deploy the plugin into Visual Paradigm, you can then click the plugin button in the application toolbar to trigger it.
Download Sample Plugin
You can click this link to download the sample plugin.
Related Know-how |
Related Links |




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!