When your project is simple, you are able to express all of the design ideas with just a few diagrams. The diagrams are simple and self-explanatory. Each of them represents a distinct design idea and there is no overlapping between diagrams.
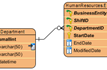
When you are dealing with a complex project, you may need to draw multiple diagrams to represent different contexts. You need to borrow shapes from a diagram to make them appear in other diagrams (i.e. contexts). In fact, this is extremely common when modeling with class diagram and business process diagram. Take UML class diagram as an example, there may be a domain diagram that presents all the entity classes and, another diagram that presents the associations and dependencies between a specific controller class and its related entity classes. So in this case, both diagrams contain the same set of entity classes.
Instead of re-creating those classes again and again in different diagrams, Visual Paradigm allows you to “re-use” them. Through simple copy and paste (Ctrl-C and Ctrl-V), you can easily copy a shape from one diagram to another. Each shape is formally known as a “view”. So with this, you can create multiple views for a model element in representing different contexts. Changes made on a shape are all synchronized to other instances that appear in other diagrams without extra effort. This is great, but there is a drawback though.
Read more



 The
The 
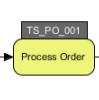 ID is a very useful property for a model elements. Having an unique ID for your model elements not just can ease the communication between your team but also help to structure your model in a more systematic way.
ID is a very useful property for a model elements. Having an unique ID for your model elements not just can ease the communication between your team but also help to structure your model in a more systematic way. 